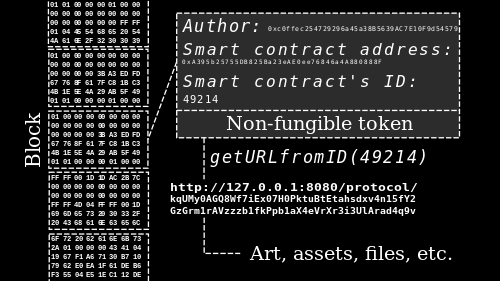
NFTs are commonly used as a digital method for verifying ownership and provenance of blockchain-registered assets. In many implementations, the creator can define what rights or utilities are associated with ownership, such as access, licensing terms, or participation benefits. The blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of ownership history, making NFTs particularly useful in environments where authenticity, traceability, and scarcity are important.
NFTs became widely known through their adoption in digital art and collectibles, but their applications extend far beyond artwork. They are increasingly used for digital memberships, event access, gaming assets, virtual real estate, brand engagement, and token-gated experiences. As blockchain technology continues to mature, NFTs are being explored as foundational components for digital identity, decentralized commerce, and ownership models within online ecosystems.
NFTs are commonly used as a digital method for verifying ownership of blockchain-registered assets.
In many implementations, the creator can define what rights or utilities are associated with ownership, such as access, licensing terms, or participation benefits. The blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of ownership history, making NFTs particularly useful in environments where authenticity, traceability, and scarcity are important.
As blockchain technology continues to mature, NFTs are being explored as foundational components for digital identity, decentralized commerce, and ownership models within online ecosystems. NFTs function as programmable digital assets, meaning they can include embedded logic that defines how they behave once issued. This can include automatic royalty payments to creators on secondary sales, access controls to private platforms or communities, and integration with decentralized applications. Because NFTs operate on smart contracts, they can interact with other blockchain-based systems without intermediaries, enabling new forms of digital commerce and ownership.
A key advantage of NFTs is verifiable scarcity. Creators can limit supply, issue editions, or design tokens with evolving attributes, all enforced by the blockchain. This capability has made NFTs valuable in ecosystems where rarity and provenance matter, such as digital art, gaming items, virtual worlds, and branded digital goods. Unlike traditional digital files, NFTs allow scarcity to exist natively in digital environments.
NFTs also support interoperability across platforms. A single NFT can be recognized and used across multiple marketplaces, wallets, games, or applications, depending on how it is designed. This allows users to retain control of their assets independently of any one platform, aligning with the broader principles of decentralization and user ownership that underpin blockchain technology.
In business and enterprise contexts, NFTs are being explored for use cases such as digital licensing, certification, loyalty programs, and access management. Because ownership and transfer history are publicly verifiable, NFTs can reduce friction in authentication and distribution processes while enabling new revenue and engagement models.
As infrastructure and standards continue to improve, NFTs are increasingly viewed not only as collectibles, but as a foundational building block for digital ownership, identity, and value exchange in decentralized systems.
In many implementations, the creator can define what rights or utilities are associated with ownership, such as access, licensing terms, or participation benefits. The blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of ownership history, making NFTs particularly useful in environments where authenticity, traceability, and scarcity are important.
As blockchain technology continues to mature, NFTs are being explored as foundational components for digital identity, decentralized commerce, and ownership models within online ecosystems. NFTs function as programmable digital assets, meaning they can include embedded logic that defines how they behave once issued. This can include automatic royalty payments to creators on secondary sales, access controls to private platforms or communities, and integration with decentralized applications. Because NFTs operate on smart contracts, they can interact with other blockchain-based systems without intermediaries, enabling new forms of digital commerce and ownership.
A key advantage of NFTs is verifiable scarcity. Creators can limit supply, issue editions, or design tokens with evolving attributes, all enforced by the blockchain. This capability has made NFTs valuable in ecosystems where rarity and provenance matter, such as digital art, gaming items, virtual worlds, and branded digital goods. Unlike traditional digital files, NFTs allow scarcity to exist natively in digital environments.
NFTs also support interoperability across platforms. A single NFT can be recognized and used across multiple marketplaces, wallets, games, or applications, depending on how it is designed. This allows users to retain control of their assets independently of any one platform, aligning with the broader principles of decentralization and user ownership that underpin blockchain technology.
In business and enterprise contexts, NFTs are being explored for use cases such as digital licensing, certification, loyalty programs, and access management. Because ownership and transfer history are publicly verifiable, NFTs can reduce friction in authentication and distribution processes while enabling new revenue and engagement models.
As infrastructure and standards continue to improve, NFTs are increasingly viewed not only as collectibles, but as a foundational building block for digital ownership, identity, and value exchange in decentralized systems.